Biacore X100 reference portal
Principles of kinetic analysis
![]()
where ka is the association rate constant (M-1s-1)
and kd is the dissociation rate constant (s-1)
![]()
During sample injection, the concentration of free analyte [A] is kept constant by continuous supply of new sample. We call this value C.
The concentration of complex on the surface [AB] is given in resonance units (RU) by the response above baseline. We call this value R.
The concentration of free ligand on the surface [B] is not measured directly. However, the total ligand concentration can be expressed in resonance units as the maximum analyte binding capacity Rmax and the concentration of free ligand is then Rmax-R.
The net rate of complex formation during injection is given by
![]()
Determination of kinetic rate constants
The figure above shows how the terms in the net rate expression relate to the sensorgram. Rmax is the maximum binding level of analyte, when all target/ligand sites are occupied. At each time point, the concentration of free/unoccupied ligand can be expressed as Rmax-R. The change in response over time (dR/dt) is given by the slope of the curve.
Substituting appropriately in the general equation for binding kinetics gives the corresponding equation for Biacore:
![]()
Since the terms R and Rmax are both measured in RU, it does not matter that the molar concentrations of ligand and complex on the surface are not known. The concentration of analyte C must however be known in molar terms.
After the sample has passed over the surface, analyte that dissociates from the complex is carried away by the buffer flow, so that the free analyte concentration is zero. The rate of dissociation is then described by the equation
![]()
Note that this equation is independent of the concentration of analyte in the sample.
This theoretical treatment applies to the ideal case of a homogeneous 1:1 interaction between ligand and analyte, with a fully efficient supply of analyte during the sample injection and a fully efficient removal of free analyte in the dissociation phase.
Experimental situation may deviate from this ideal. Some causes of deviations are mass transport limitations (less than 100% efficient supply and removal of analyte), heterogeneous samples, multivalency and complex interaction mechanisms.
Information in a sensorgram
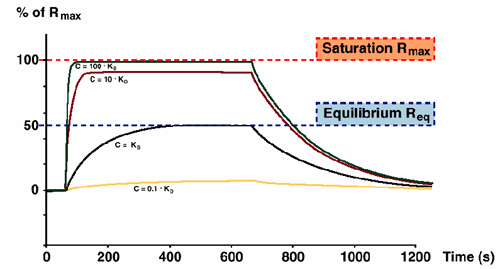
The sensorgram contains information about association and dissociation rates, and also equilibrium levels (steady-state) if a plateau is reached during sample injection. Plateau levels Req at high analyte concentrations approach maximum binding capacity Rmax (100x KD or higher). KD is the analyte concentration that gives half-maximal saturation (Req = Rmax/2).
It is important to note that Req can be reached at several levels depending on the concentration. It is however only when the Req = Rmax/2 that the concentration equals KD.
Difference between affinity and kinetics
Affinity does not always tell the entire story. Interactions with the same affinity may have entirely different kinetic rate constants, which could have an impact on the biological significance and behavior.
Compounds with slow dissociation rate (such as the red and yellow curves in the figure below) occupy the target for a longer time. The analyte concentration in the right overlay plot is ten times higher than in the left plot. This shows that the increase in concentration affects the association phase, while the dissociation phase is independent of the concentration. Rmax (when all binding sites are occupied) is reached for all curves except for the red one at the higher concentration. The figure below also shows the difference between Rmax and Req. In the left plot, the plateau that is reached by the black and green curves represents the equilibrium level, while the plateau for the same curves at the higher concentration represents the Rmax level.
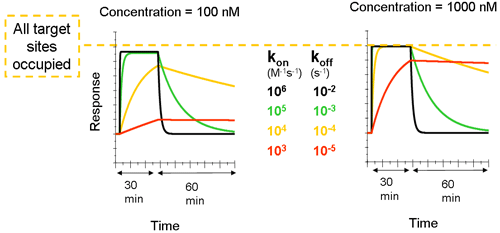
This figure also shows the difference between Rmax and Req. In the left plot, the plateau that is reached by the black and green curves represents the equilibrium level, while the plateau for the same curves at the higher concentration represents the Rmax level.
Measure kinetics and affinity in Biacore
There are three ways to obtain kinetic and affinity data in Biacore:
- Monitor association and dissociation rates
Analyzing association and dissociation rates for a series of analyte concentrations gives kinetic information which can also be expressed as affinity and steady state does not have to be reached. - Monitor steady state levels
Analyzing steady state levels as a function of analyte concentration gives affinity values but not kinetics. It is useful for fast on-fast-off interactions where kinetics cannot be determined. Limited usefulness for slower reactions because of the time taken to reach steady state. - Measure free analyte in solution
Measures affinity in solution: allow mixtures of interactants to reach equilibrium in solution and use Biacore to measure the concentration of free analyte in the mixtures. It can be applied to situations where direct measurement may be difficult (small molecules, interactions that are disturbed by ligand immobilization etc) and to obtain solution values for comparison with surface-bound values.
 Kinetics and affinity |
 Affinity only |
Panel 2 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 3 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.

Panel 4 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 4 header 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header 3
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.