Biacore X100 reference portal
Immobilization approaches
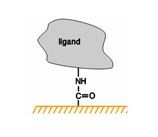
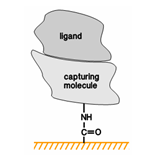
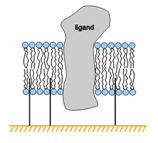
Molecules can be attached to the chip surface using several techniques, including covalent immobilization using a variety of chemical methods, high affinity capture to a specific capturing molecule and adsorption of lipid mono- or bilayers.
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
For most protein ligands, amine coupling is the simplest approach, although it is not necessarily the most effective. For some proteins, thiol coupling can give better yields of immobilized ligand. Acidic proteins which are not efficiently pre-concentrated in their native state can be modified with PDEA for surface thiol coupling: this reaction modifies carboxyl groups on the protein, raising the isoelectric point of the protein and facilitating immobilization.
In cases where amine or thiol coupling is not satisfactory, either because yields are too low or because the coupling procedure inactivates the protein, biotinylation followed by capture on a streptavidin surface can often provide an alternative approach. Biotinylation can be performed using mild reaction conditions. If a specific high-affinity interactant such as an antibody is available, capturing through this interaction may be preferable since modification of the ligand with biotin is avoided.
Capture through streptavidin-biotin interaction is also the method of choice for immobilizing nucleic acids, which are easily biotinylated and which are generally not amenable to amine or thiol coupling chemistry. In addition, capturing methods are much less dependent on electrostatic pre-concentration, which is inefficient for nucleic acids.
Some biomolecules, notably carbohydrates and glycoconjugates, may be successfully immobilized using aldehyde chemistry after oxidation of cis-diols in the ligand to aldehydes.
Covalent immobilization of ligand on the surface exploits the carboxyl groups on CM-dextran sensor chips and allows preparation of robust surfaces with very little consumption of ligand.
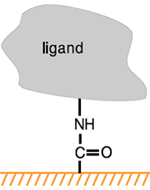
Covalent immobilization generally results in stable attachment of the ligand to the surface under the buffer conditions normally used for interaction analysis and surface regeneration. Regeneration of the surface removes bound analyte at the end of each analysis cycle but leaves the ligand attached to the surface. Some covalent coupling methods may have limited stability under certain conditions: thiol-disulfide exchange coupling, for example, is not suitable for attaching ligands that are to be studied in the presence of reducing agents.
Although covalent immobilization involves chemical modification of the ligand which can potentially affect the analyte-binding activity, most ligands can be immobilized by one or another chemistry without losing activity. In cases where covalent attachment does result in loss of ligand activity or is unsuitable for other reasons, capturing provides an alternative approach.
Immobilization chemistries
A range of immobilization chemistries can be used:
- Amine coupling: The most generally applicable approach for protein ligands. Uses primary amines on the ligand for the immobilization.
Read more: Amine coupling - Surface thiol coupling: Uses thiol-disulfide exchange between thiol groups on the surface matrix and reactive disulfide introduced to the ligand for the immobilization.
Read more: Surface thiol coupling - Ligand thiol coupling: Uses thiol-disulfide exchange between reactive disulfides on the surface and thiol groups on the ligand.
Read more: Ligand thiol coupling - Maleimide coupling: Uses maleimide reagents to mediate immobilization via thiol groups on the ligand. Provides an alternative to thiol-disulfide exchange in experiments that require reducing conditions.
Read more: Maleimide coupling using sulfo-GMBS, Maleimide coupling using EMCH or BMPH - Aldehyde coupling: Uses aldehyde groups to immobilize the ligand. This approach can be useful for immobilization of carbohydrates and glycoproteins.
Read more: Aldehyde coupling
Ligand orientation
The site of immobilization on the ligand molecule – and therefore the orientation of the immobilized ligand – cannot usually be determined with approaches like amine coupling that address multiple targets in the ligand (most proteins contain several available amine groups). Thiol coupling will often give more homogeneous ligand immobilization since thiol groups are generally less common than amines. Protein engineering can be used to introduce single thiol groups into ligands that lack thiols in their naturally occurring form. Capturing approaches can provide an alternative if homogeneous orientation of the ligand is important for the experimental design.
Panel 2 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 3 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.

Panel 4 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 4 header 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header 3
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.