Biacore X100 reference portal
CFCA
Calibration-free concentration analysis (CFCA) is an approach to measuring analyte concentration with Biacore systems that does not require any calibration standards. The method relies on measuring the rate of binding under conditions where the rate is limited by diffusion of analyte to the surface and is independent of the interaction kinetics. Diffusion-controlled binding rates are directly proportional to the analyte concentration and are independent of interaction kinetics.
CFCA gives an absolute value for analyte concentration in weight-based or molar units. Note that as with any interaction-based concentration assay, the values obtained represent the concentration of active analyte molecules, as defined by their ability to interact with the surface-bound ligand.
Uses
CFCA is useful for
- determining the concentration in absolute terms for analytes for which calibration standards are not available.
- determining the amount of active analyte in calibration standards (i.e. determining the activity of the standards) in order to validate a calibrated assay. The effect of partial activity in calibration standards on the results of a calibrated assay is illustrated here:
Partially active calibration standards
If the calibration standards used in a concentration assay are only partially active in terms of binding to the ligand, the assay results will be distorted.
Consider the situation where the calibration standards are only 80% active. A nominal standard concentration of, say, 1 nM will give a response that actually represents only 0.8 nM of active calibrant. A sample that gives the same response will contain 0.8 nM active analyte but will be reported as 1 nM. The accuracy of the reported value will depend on the active fraction in the sample, as illustrated in the table below.
Effect of partial activity of standards on the accuracy of calibrated concentration measurements.
 Calibrant
Calibrant
80% activeSample 1
100% activeSample 2
50% activeCalibrant concentration1 nM----True active concentration0.8 nM0.8 nM0.8 nMReported concentration--1 nM1 nMTrue total concentration1 nM0.8 nM1.6 nM
- determining the true active concentration of analyte for robust measurement of kinetic and affinity constants.
Limitations
The requirement for measuring binding under conditions of limiting analyte diffusion imposes the following limitations on the method:
- High ligand immobilization levels are desirable. As a rule of thumb, do not immobilize less than 25 RU per 1000 Da ligand molecular weight (e.g. for a ligand of 150,000 Da, immobilize at least 3,750 RU. Immobilization levels of 5-10,000 RU are preferable for average-sized proteins).
- The usable range for the measured analyte concentration is limited to about 0.5-50 nM. Samples outside this range should be diluted or concentrated as appropriate for reliable measurement.
- Analytes smaller than about 5000 Da cannot be measured reliably.
- Analytes with slow association rates (ka < 105 M-1s-1) and/or low affinity (KD > 10-6 M) are not suitable.
Evaluation of CFCA uses double-referenced data where possible (i.e. reference-subtracted and blank-subtracted sensorgrams). Concentrations are determined by fitting the data to a model for mass transport-limited interaction, using values for the mass transport coefficient km calculated from the provided values for analyte diffusion coefficient and molecular weight:![]()
where:
D is the diffusion coefficient of the analyte
f is the flow rate of solution through the flow cell
h, w, l are the flow cell dimensions (height, width, length)
Assessing the sensorgram data
Before applying the evaluation, assess the sensorgram data for quality and suitability.
- Sensorgrams at the lower flow rate should be approximately linear throughout the sample injection (with allowance for short disturbances at the beginning and end of the injection). Exclude cycles with obviously disturbed sensorgrams, or with sensorgrams that show significant curvature at the lower flow rate.
- Examine the initial flow rate. The initial binding rate at a flow rate of 10 µl/min should be within a range from about 0.3 RU/s to a value given by the analyte molecular weight divided by 10,000 (e.g. for an analyte of molecular weight 150,000, the acceptable range is about 0.3-15 RU/s). Exclude cycles where the initial rate is clearly outside this range.
- Examine the QC ratio values. The QC ratio is an indicator of the extent to which the initial binding rate is influenced by flow rate. Exclude samples with a QC ratio of less than about 0.2.
QC ratio for CFCA
The QC ratio calculated for CFCA evaluation is an indicator of the extent to which the measured initial binding rate is influenced by flow rate.
The quotient Q is set to the ratio of the initial binding rates at high and low flow rates, multiplied by the inverse ratio of the cube roots of the flow rates themselves: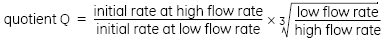
Binding that is entirely limited by interaction kinetics is independent of the flow rate, so that the quotient Q for interaction-limited binding (denoted Qmin) is the cube root of the flow rate ratio. For flow rates of 10 and 100 µl/min, this value is 0.46 (the cube root of 0.1).
For binding that is completely limited by mass transport, the binding rate is proportional to the cube root of the flow rate, giving a maximum value for Q (Qmax) of 1.
The QC ratio expresses the measured difference in binding rates as a fraction of the theoretical maximum difference: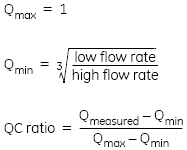
Assessing the evaluation results
A concentration value is reported for all samples that are evaluated. Use these guidelines to assess whether the concentration is reliable:
- Check the appearance of the sensorgrams and fitted curves. Reject samples where the fit is poor.
- Check the value for SE (Conc) or T (Conc). This value represents the statistical significance of the calculated concentration. Reject samples where the standard error is more than about 20% of the calculated concentration (or correspondingly a T-value that is lower than about 5).
- Check the QC ratio. Reject samples with a QC ratio of less than about 0.2.
- The optimal concentration range that can be measured with calibration-free concentration analysis is 0.5-50 nM. Values outside this range should be treated with caution. (The calculated concentration may be outside this range if you have diluted your samples.)
- If you have analyzed duplicates and/or several dilutions of the same sample, check the agreement between calculated concentrations.
Surface preparation
Use a high level of immobilized ligand to help ensure mass transport limited analyte binding. As a rule of thumb, do not immobilize less than 25 RU per 1000 Da ligand molecular weight (e.g. for a ligand of 150,000 Da, immobilize at least 3,750 RU. Immobilization levels of 5-10,000 RU are generally preferable for average-sized proteins).
Samples
- CFCA is not suitable for analytes with molecular weight below about 5000 Da.
- The working range of the CFCA assay is approximately 0.5-50 nM, with best results at about 5 nM. If you have no idea of the sample concentration, prepare a 10-times dilution series in running buffer with a total of 4 samples (covering the original sample to 1000-times diluted). This will often give at least one measurable concentration, or at least give an indication of a suitable dilution.
Setup
- Run each sample at two widely separated flow rates (recommended 5-10 and 100 µl/min). Assay wizards for CFCA fulfil this requirement automatically. For custom methods, you will need to set the flow rates explicitly.
- Running the samples at several dilutions (serial dilution factor 5 or 10) can help in assessing the validity of the results.
- Run duplicate determinations if time and material allow.
- Include at least one blank sample analyzed at the same flow rates as the samples. Subtraction of the blank cycles improves the robustness of the evaluation.
- Provide values for the analyte molecular weight and diffusion coefficient at 20°C. These values are required for evaluation of the results. The diffusion coefficient value is automatically converted to the analysis temperature in the evaluation software. Diffusion coefficients can be obtained from the literature or calculated from the molecular properties of the analyte using the Diffusion Coefficient Calculator available on the Cytiva web site.
Panel 2 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 3 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.

Panel 4 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 4 header 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header 3
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.