Biacore X100 reference portal
Biotinylation for streptavidin-biotin capture
Biotinylation of proteins and peptides provides a convenient way preparing molecules for permanent capture by high affinity binding to Sensor Chip SA or reversible capture on Sensor Chip CAP using the Biotin CAPture kit.
Reagents
A range of methods and commercial reagents for ligand biotinylation is available: the choice of method will depend largely on the nature of the ligand. Many are directed towards attachment of biotin to amine groups using NHS-based chemistry, but reagents are also available for biotinylation of other target groups.
Some reagents include a spacer between the target molecule and the biotin residue. This has been found to improve both immobilization yields on Sensor Chip SA and accessibility of analyte-binding sites on the immobilized ligand for some protein ligands.
Procedures
Substitution levels around 1 biotin residue per ligand molecule are recommended for capture on streptavidin. In general, the conditions recommended for biotinylation of proteins with commercial reagents tend to give higher substitution levels, resulting in multi-point attachment of the ligand to the surface with possible impairment of assay performance. If the reagent supplier does not provide guidelines for regulating the level of substitution, try using lower reagent concentration and/or shorter reaction times. A molar ratio of 1.5:1 between reagent and target molecule often works well.
It is very important that excess biotinylation reagent is removed from the ligand before capture on streptavidin. Desalting columns are generally suitable for macromolecular ligands. More selective chromatographic techniques such as higher resolution gel filtration or reversed phase chromatography can be used for smaller ligands.
Determining the degree of biotinylation
Measuring the degree of biotinylation is a valuable guideline to finding and confirming modification conditions, but does not provide any information on the efficiency of ligand attachment to the sensor chip or the analyte-binding activity of the biotinylated ligand. These parameters can only be determined by testing the ligand preparation in a Biacore assay.
Several methods are available for determining the level of ligand biotinylation. Spectrophotometric methods based on displacement of bound chromophores from avidin by the biotinylated ligand (e.g. the HABA method using 4'-hydroxyazo-benzene-2-carboxylic acid 1) are generally easy to perform but have low sensitivity and require relatively large quantities of biotinylated ligand. More sensitive assays based on e.g. enzymatic, chemiluminescent or fluorescent detection are valuable when the amount of ligand is limited. Biotinylation reagents are also available with a chromophore built in to the spacer, allowing direct spectrophotometric determination of biotinylation levels (e.g. biotin-X 2,4-dinitrophenyl-X-L-lysine, succinimidyl ester from Molecular Probes Inc or ChromaLink Biotin354S from Solulink Biosciences Inc). Detailed descriptions of a variety of methods may be found in the literature.2
Troubleshooting tips
Observe the following points for best results:
- Determine the ligand concentration as accurately as you can, so that the amount of biotinylation reagent can be adjusted accordingly and the same conditions can be reproduced for new batches of ligand.
- Use carefully controlled temperature and incubation time for the biotinylation reaction so that the same conditions can be reproduced.
- Remove all excess biotinylation reagent after the reaction is complete. Residual reagent will compete with ligand for attachment to the sensor chip.
If you have problems with low attachment yields of biotinylated ligand on the sensor chip, consider the following:
|
Cause of low yields
|
Corrective action
|
|
Biotinylation level too low
|
Increase the molar ratio of biotinylation reagent to ligand during biotinylation.
Use a different biotinylation chemistry or reagent if increasing the reagent concentration is not sufficient. |
|
Ligand concentration too low
|
Start with a higher ligand concentration or optimize the buffer exchange and reagent removal steps.
|
|
Injection time too short
|
If the sensorgram has not reached a plateau during ligand injection, you can inject more ligand over the same chip to increase the attachment yield.
|
|
Unsuitable biotinylation buffer
|
Avoid amines (e.g. Tris, sodium azide) for biotinylation of amine groups, and corresponding components for other reagents. Include a buffer exchange step before biotinylation if necessary.
|
|
Free biotin present in ligand solution
|
Repeat the reagent removal step.
|
1 Cifonelli, J. A. (1968), Carbohydrate Research 8, 233.
2 See for example Methods in Enzymology vol. 4 (1988).
Lab protocol
Lab procedure Biotinylation for streptavidin/neutravidin-biotin capture on Biacore sensor chips is available for download on www.cytivalifesciences.com/solutions/protein-research/Interaction-analysis-with-Biacore-surface-plasmon-resonance-SPR/Get-started-with-surface-plasmon-resonance-SPR-interaction-analysis
Sensor Chip SA provides a sensor surface with covalently attached streptavidin, designed for capture of biotinylated compounds. The affinity of streptavidin (or avidin) for biotin is extremely high, with an equilibrium dissociation constant of about 10-15 M, and dissociation of biotinylated ligands from the surface of Sensor Chip SA is generally negligible during the course of a Biacore analysis. Reagents and methods for introducing biotin into a range of molecules including nucleic acids, lipids, proteins and carbohydrates are readily available, and capture of biotinylated ligands on Sensor Chip SA is usually a simple and reliable procedure.
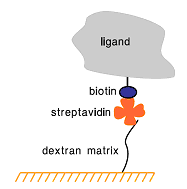
Capture of biotinylated ligands on a streptavidin surface is a special case of the capturing approach, since the streptavidin-biotin interaction is so tight that the capturing is essentially irreversible. Removal of the ligand in the regeneration step is not usually feasible, and regeneration is normally directed towards removing bound analyte while leaving the biotinylated ligand on the surface. In this respect, streptavidin-biotin capture is more similar to covalent attachment than to other capturing approaches.
Panel 2 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 3 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.

Panel 4 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 4 header 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header 2
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.
Panel 5 header 3
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Repellendus aliquid tempore natus voluptates repudiandae, eos dolorem libero inventore, quod incidunt, asperiores. Reiciendis itaque enim pariatur, blanditiis minima autem quo a nulla, obcaecati quis, excepturi atque ab rerum! Sequi molestias vel eum, hic, perspiciatis eius suscipit reprehenderit molestiae vitae similique.